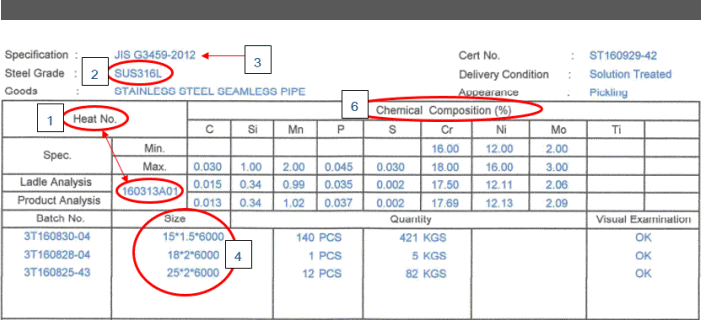
What Is a Heat Number?
A heat number is a unique identifier stamped on a piece of metal to give information about its origin. Metal pipes, flanges and fittings, etc. are stamped with this number, and in some cases it is required by law to be used on metal products.
The heat number provides a method of tracing materials and is an important part of quality assurance and control. Commonly, people can find it near the edge or end of a finished metal piece, and there may also be other information on the stamp.
Quality control involves subjecting a piece of metal from a given batch to tests to make sure it meets all requirements. It is tested for contaminants, weaknesses and other problems. If there is a problem with the metal, other pieces with that heat number can be recalled to check them and see if they have the same problem. The number also matches data about the crew that handled the metal, the time it was cast, and so on. This information can be useful when determining why the same quality control problem keeps recurring.

The heat number allows all materials from a particular factory to be traced. Along with the heat number, the stamp includes an indication of the manufacturer and factory, if the manufacturer has more than one metalworking plant. The stamp may also include the die number, which refers to the die the company used to make the product. This can be useful for matching replacement parts because the die number can be used to get an exact replacement.
Manufacturers may apply the heat number even if the law does not require it, because it can be a useful tool to verify materials. As long as the company keeps current records, it should be able to look up any piece of metal by its heat number and provide insight into its origin. This can be useful for activities such as accident forensics, where investigators want to know more about a particular metal product to see if a problem with the metal contributed to the accident. Heat numbers are also useful for recalls, allowing people to identify a bad batch of metal and alert the public.
Difference between Heat No. and Lot No.
Heat number refers to the identification number assigned to a specific batch of raw material used in the production process (each melt produced each time in a steel production furnace represents one heat).
Lot number refers to a specific quantity of a product (specific lot) produced at one time that has a unique identification number. It is used in the production of products such as pharmaceuticals, food and chemicals. Lot number helps in tracking the production process and ensures that products are made according to the required specifications.
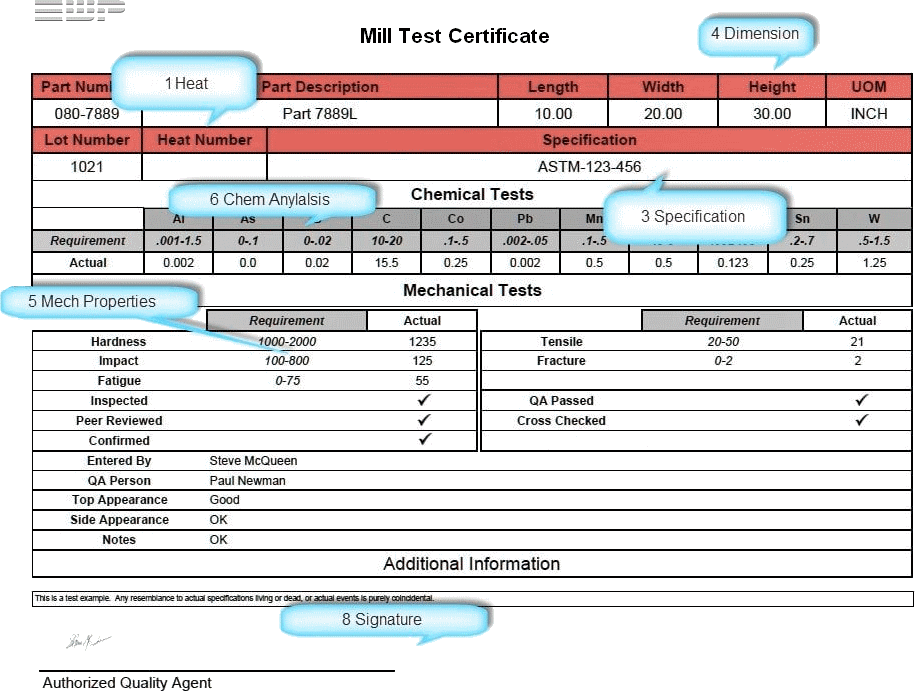
Mill Test Certificate
 Mill Test Certificate
Mill Test Certificate
The Mill Test Certificate (MTC), also known as a material test report, is a document that verifies the chemical and physical properties of a material. Usually, the report is written on paper and contains the approval of the factory quality control along with a special stamp of the material test certificate.
The test standards and content of the report usually correspond to the factory's production standards or the customer's specific requirements. The report contains detailed information about the material's composition, including type, quality and specification, as well as the results of various tests the material was subjected to, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and the heat number of the material in question.
Related Post(s)
This article introduces you to material test certificates, explains their meaning and outlines issues you may encounter with your manufacturer or supplier...