What is a cooling tower?
Cooling towers are a special type of heat exchanger in which water and air interact to lower the temperature of hot water. During cooling tower operation, small amounts of water evaporate, lowering the temperature of the water circulating through the cooling tower.
In a nutshell, the purpose of a cooling tower is to cool water heated by industrial equipment and processes. The water enters the cooling tower hot (from the industrial process) and exits cold (back to the industrial process).
How Do Cooling Towers Work
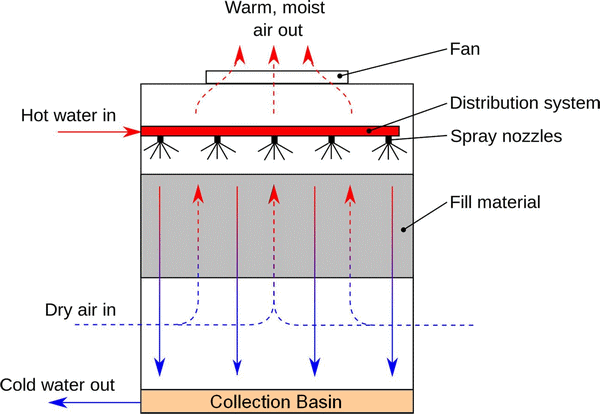
The hot water is usually caused by condensers from air conditioning or other industrial processes. That water is pumped through pipes directly into the cooling tower. Cooling tower nozzles are used to spray the water onto the "filling medium," slowing the flow of water and clearing as much water surface as possible for optimal air-water contact. The water is exposed to air as it flows through the cooling tower. The air is drawn in by a motor-driven electric "cooling tower fan."
When the air and water come together, a small amount of water evaporates, creating a cooling effect. The colder water is pumped back to the process/equipment that absorbs heat or the condenser. The loop is repeated over and over to constantly cool the heated equipment or condensers.
There are many different types of cooling towers, but the operating principles of cooling towers remain pretty much the same. Most cooling towers operate on the principle of "evaporative cooling".

What is evaporative cooling?.. evaporative cooling is the process of pumping hot water from an industrial process to the top of the cooling tower, where the water distribution system is located. The water is then distributed through cooling tower nozzles to the wet deck. At the same time, air is drawn in through the air intake vents, causing the water to evaporate. evaporate. Evaporation removes heat from the makeup water. Warm air rises naturally from the tire.
What are cooling towers used for?.. an HVAC cooling tower is used to dissipate or repel heat from chillers. Air-cooled chillers are less efficient than water-cooled chillers because of the heat dissipation of the water from the cooling tower at wet-bulb temperatures.
Cooling tower applications.. traditional HVAC heating and cooling systems are used in schools, large office buildings and hospitals. Cooling towers, on the other hand, are much larger than traditional HVAC systems and are used to remove heat from cooling tower systems in petroleum refineries, factories, natural gas processing plants, petrochemical plants and other industrial processes and facilities.
Types Of Cooling Tower Systems
Cooling towers are usually designed for specific purposes. Not all cooling towers work for all applications or industrial processes.
- Crossflow Cooling Towers
- Counterflow Cooling Towers
- Forced Draft and Induced Draft Cooling Towers Process
- Factory Assembled Cooling Towers (FAP) Factory Assembled Product
- Field-Erected-Towers (FEP) Field Erected Product
Cross-flow cooling towers.. in cross-flow cooling tower systems, water flows vertically through the filling medium while air flows horizontally over the falling water. That's why they call it crossflow because the air and water cross. Because the flows cross, the air does not have to pass through the distribution system. This allows hot water to be used through gravity and distribution basins at the top of the tower, right above the filling media. The basins are a standard of cross-flow cooling towers and are applied to all units.
Counterflow cooling tower.. difference between crossflow and counterflow cooling towers... In a counterflow cooling tower system, the air flows vertically upward, against the flow of water into the filling medium. Because the air flows vertically, it is not possible to use the gravity flow of the basin, as in cross-flow towers. Instead, these towers use pressurized spray systems, usually of the tube type, to spray the water on top of the filling medium. Cooling tower tubes and nozzles are usually spaced farther apart so they do not obstruct air flow.
Forced Draft and Induced Draft Cooling Towers Process.. cooling tower fans are used on cooling towers with induced draft to pull air up through the filling medium. On cooling towers with induced draft, air is pushed/forced by fans at the bottom of the air inlet valve.
Factory Assembled Cooling Towers (FAP) Factory Assembled Product.. these factory-assembled cooling tower systems are delivered somewhat disassembled in a few parts, ready for final assembly or on-site assembly. However, small factory-assembled cooling towers can be shipped intact. FAP cooling towers can be induced draft, crossflow, forced draft or counterflow, depending on the application for which they are needed.
Field-Erected-Towers (FEP) Field Erected Product.. field cooling towers are usually built on site. The large FEP is usually prefabricated, marked by piece and shipped to the construction site for assembly. The cooling tower manufacturer usually handles the entire cooling tower construction process and final assembly. These types of towers can be counterflow or crossflow cooling towers, depending on the application. For heavy industrial applications or when more power is needed, cooling towers can be built on site to exact specifications, structure, performance, plume control and drift.
