Peristaltic Pump
Peristaltic pumps are a type of rotary positive displacement pump that consist of two integral parts.. a rotor with a number of rollers or a "shoe" attached to it and a flexible internal hose/tube attached in a round pump housing.
Therefore, this pumping technology is also called peristaltic pump. There are two different operating mechanisms of peristaltic pumps: roller and shoe peristaltic pumps.
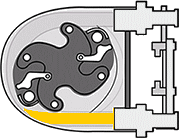
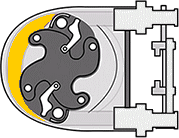
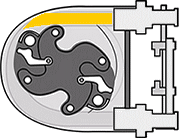
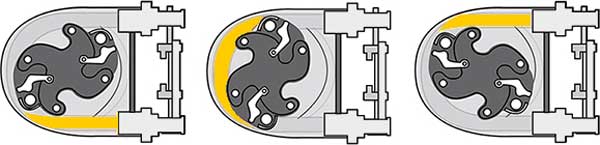
Roller-driven peristaltic pumps
As the rotor rotates, the attached rollers compress the hose in which the fluid is located, and it is this action that forces the fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump. Because the rollers generate less friction than shoe designs, such peristaltic pump models have..
- Lower power consumption, with up to 30% energy savings compared to peristaltic shoe pumps
- Low starting torque - smoother operation and easier speed adjustment
- Simpler hose maintenance because no lubrication is required
Shoe operated peristaltic pumps
As the rotor rotates, the attached shoe compresses the hose in which the fluid is contained, and it is this action that moves the fluid from the inlet of the pump to the outlet. This version is ideal for heavier applications with higher pressures, where roller models cannot handle the application efficiently. These models have casings filled with lubricant to prevent wear on the outside of the internal hose, which must be maintained.
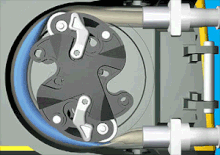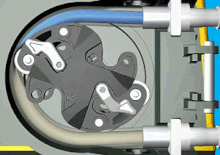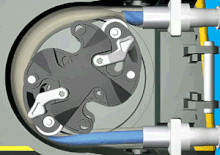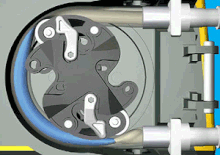

Image animation.. www.watson-marlow.com
Design advantages
Different fluids - Since the only part of the peristaltic pump that comes in contact with the pumped fluid is the flexible inner hose, only the material of the hose needs to be compatible with the fluid instead of having to consider o-rings, seals and valves as well. This makes it a versatile solution for many fluids by changing the material of the inner hose..
- Natural rubber (NR) - for water-based liquids
- Neoprene (CR) - Good balance between chemical and mechanical resistance
- EPDM - Ideal for hot liquids and clean in place applications, acids and alkaline
- Silicon (VMQ) - best for very high temperatures
- Nitrile (NBR) - for greases, fuels and oils
Leak-free - Because the pumped liquid remains within the inner hose, peristaltic pumps do not require a seal. The absence of a seal makes this pump type less likely to leak, making it an ideal solution for handling corrosive liquids and hazardous chemicals and where cleaner and safer operation is generally required.
Excellent solids handling and non-clogging - In addition to the above, peristaltic pumps are suitable for tough applications, such as those involving viscous slurries and solids, because the liquid is restricted only by the inner hose and there are no valves and seals to clog. This means that peristaltic pumps can pump solids and sharp and stringy particles without clogging up to the diameter of the inner hose.
Low shear - Hose pumps benefit from gentle pumping motion and low speed. Because the pump performs low shear movements, the structure of the fluid does not change, making the design ideal for handling delicate, shear-sensitive fluids damaged by other pump types.
Reversible operation - This allows pumping from tank to tank, i.e. filling and emptying, and retrieving the fluid from the hoses at the end of dispensing. This is particularly beneficial for peristaltic pumps used in mobile applications, where the tubing is periodically removed to move the pump, to ensure no liquid leaks from the end.
Typical applications of a peristaltic pump - Peristaltic pumps are the ideal solution where other pumps fail. Their ability to handle highly viscous or solids-laden mediums without damage, their easy and inexpensive maintenance and their ability to run dry makes them a popular choice for heavy and abrasive applications. Moreover, the wide variety of materials in which the inner tube is available, along with the sealless design of the peristaltic pump, means that even the most aggressive fluids and chemicals can be handled.
Given the above design advantages, peristaltic pumps are ideal for the following (and many more) high and low flow applications..
- Pumping of mortar, cement, clay and mud
- Wastewater and excavation dewatering
- Pumping of wastewater and sludge
- Food and beverage production
- Paint, ink, pigment and dye
- Oil sludge and waste oil
- Pulp and paper slurries
- Chemical dosing
Good priming height and self-priming capability - peristaltic pumps can self-prime up to 8 meters. They can also run dry indefinitely without damage if the operator leaves the pump running and can handle liquids with low moisture content.
Low maintenance - Because the only wet part of the peristaltic pump design is the inner hose, wear parts are limited to this hose and thus this is the only part of the pump that requires maintenance, which can be done quickly and easily. The absence of valves, seals and glands that can clog and wear out when in contact with the pumped medium, especially abrasive media, reduces maintenance time and spare parts costs.
References..
www.castlepumps.com
www.pumpsandsystems.com
www.hydroinnovations.com.au
Peristaltic pump working principle