Laser Welding of Metals
The use of lasers is a relatively new way of welding. Although the concept is still the same - using heat to join two materials - the way heat is delivered by lasers is quite unique. Although laser welding has been around for decades, the use of this technology has only recently picked up because of the transition to automated manufacturing processes.
How does it work?
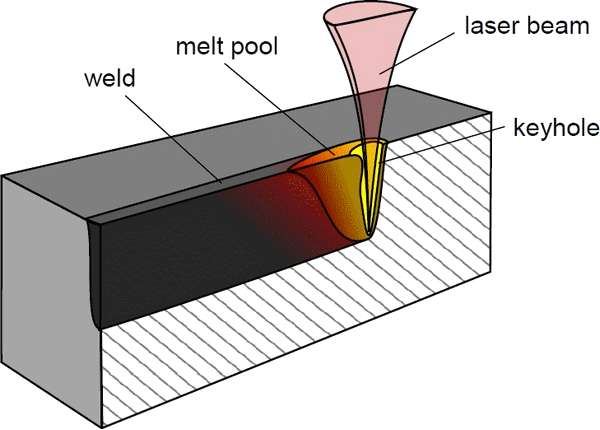
Laser welding or Laser Beam Welding (LBW) is a process in which lasers are used to melt the material on the surface of a workpiece so that it can be joined to another workpiece of the same material. Laser welding is usually applied to metals or thermoplastics. Different types of lasers are also used for welding, with older applications using solid-state lasers or gas lasers being widely used today.
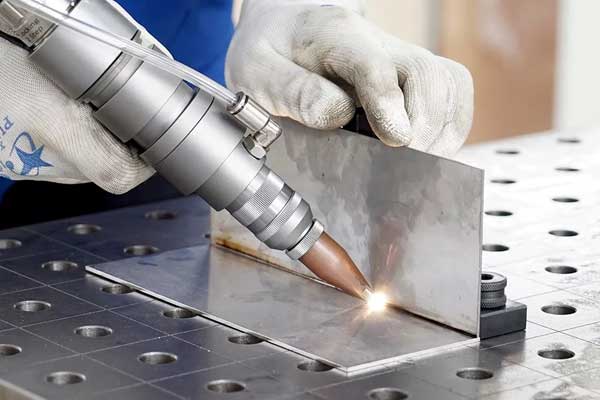 Image.. www.eetolaser.com
Image.. www.eetolaser.com
A laser is nothing more than a highly concentrated beam of light that delivers an enormous amount of power. The high power density of lasers allows them to melt the material of the workpiece in a controlled manner. By subjecting the material to a powerful laser beam, the molecules in the surface receive enough energy to be excited and acquire more fluid-like properties.
When excited molecules of the same material contact each other and simultaneously transition to lower excitation states, they become solids again and develop a bond at the molecular level.
Laser welding (like other laser technologies) was used almost exclusively in laboratories and research institutions until sometime in the late 1990s. At that time, the concept of additive manufacturing began to gain popularity.
Laser welding advantages
When considering the pros and cons of laser welding technology, it is more worthwhile to compare it to traditional welding techniques - those that use a gas flame or an electric arc. After all, these traditional welding techniques are still the most widely used and are probably the entities that laser welding faces.
Ideal for automation... that makes the switch to laser welding worthwhile is that it fits perfectly into an automated production process.
Automation of the welding process offers manufacturers a host of benefits. It reduces the need for manual operations, resulting in products with greater precision and more consistent quality. Automated systems are also much faster than human welders, which is crucial for high-volume industries.
Compatible with a wide range of materials... Traditional flame or arc welding involves adjusting the temperature of the flame or the intensity of the arc to switch from one material to another. Lasers work in much the same way in that their intensity can be adjusted to make them suitable for different materials. The main advantage of lasers in this regard is that they can have preset parameters for different materials, making switchovers much smoother.
The high power density of lasers makes them suitable for welding materials that would be challenging for other welding techniques. The list of materials that can be welded with lasers is long and includes super-strong metals such as titanium and carbon steel. In terms of pure power density, the only technology that can surpass laser welding is electron beam welding.
Very high heating... Another advantage of the high power density of a laser is that it melts material much faster than a flame or an electric arc. This allows for faster welding and stronger welds. The depth of penetration in laser welding can be controlled by adjusting the power of the laser. For very thin materials, pulses from the laser can be used to prevent damage to both the material and the machine.
Can weld joints with complex geometry... A unique feature of laser welding is that it can work remotely. The tip of the laser does not have to be close to the material to provide the power required for welding. This gives more room for manipulation of the workpiece, enabling the welding of joints with complex geometries.
Improved safety... Laser welding machines are typically fully automated and have enclosed work areas. This means that personnel no longer need to be exposed to the high temperature and particles generated during welding. For this reason alone, a laser welding machine is a worthwhile investment. Any technology that increases workplace safety and keeps personnel away from unnecessary hazards is worth considering.

Laser beam
Laser welding disadvantages
Metals can crack due to rapid cooling... anything heated quickly also cools quickly. This is also the case with laser welding. The localized release of power by the lasers means that joints are welded together fairly quickly. However, it also means that the heat in the joints is dissipated just as quickly by the material.
This causes a huge buildup of thermal stress, which not all materials can handle without being damaged. Carbon steel is a classic example of a metal that tends to become brittle and crack when cooled too quickly.
High capital requirement... this is probably the biggest hurdle standing between this technology and wider application - laser welders are expensive. This is even more noticeable when compared to older welding methods that use gas flames or electric arcs.
Welding is often seen as a craft that requires an experienced welder, but not necessarily expensive equipment. Laser welding reverses this whole perspective - the equipment is expensive but operating it does not require much skill.
Applications of laser welding
In many ways, laser welding fits virtually every application of standard, old-fashioned welding. Given the long tradition of welding as a manufacturing process, the applications of laser welding are not difficult to identify.
Laser welding has proven especially useful in heavy or large manufacturing industries. These are industries that can benefit most from the added speed and precision of laser welding.
Automobile industry
 Laser welding use in the automotive industry - Image.. www.faulhaber.com
Laser welding use in the automotive industry - Image.. www.faulhaber.com
In the automotive industry, speed and quality are probably the two most important factors to consider. Fortunately, laser welding excels in both. The tool-less operation of laser welders means less downtime for regular maintenance and tool changes.
Shipbuilding
 Shipbuilding by Laser welding - Image.. https://hexagon.com
Shipbuilding by Laser welding - Image.. https://hexagon.com
Shipbuilding is one of the most demanding industries for any process, including welding. By substituting laser welding for traditional welding techniques, the construction of steel or metal structures in ships can become faster and stronger. Laser welding's low distortion from localized heating also makes it easier to make highly accurate parts with precise dimensions.
Summary
In the field of tool fabrication, the versatility of laser welding is the feature that comes into play. Whether tools are made via subtractive or additive manufacturing. Laser welding is often used to join individual elements together and achieve the intended shape of the tool. The flexibility of laser welding when it comes to joint geometry makes it ideal for an industry that makes a wide variety of products.
These are just a few examples hundreds of other different uses of laser welding. Any type of on-site use of traditional welding will likely benefit from upgrading to a laser welding machine.
There are even 'portable' laser welding machines that use fiber laser technology, although the portability of such machines is still questionable. Lasers require a lot of power, and this huge power source makes up the bulk of these 'portable' machines. This is perhaps the only department where old-fashioned welding still wins out over laser welding, because machines for electric arc welding are very light and handy.
In many ways, laser welding seems like the sensible next level of evolution from traditional welding techniques like gas flame and electric arc. The equipment is more expensive, but laser welding is undoubtedly more energy efficient, faster and more accurate. More importantly, laser welding machines are designed to operate automatically, which is a crucial element in modern manufacturing.
Portability remains the biggest challenge for laser welding technology, especially in remote construction or repair work. Yet no obstacle is insurmountable, especially when there is industrial and commercial demand for the technology.
Related Post(s)

Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding became an overnight success in the 1940s for joining magnesium and aluminium...