Fiberglass Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
FRP vs GRP: Difference Between FRP and GRP
FRP stands for Fiber Reinforced Plastic while GRP stands for Glass Reinforced Plastic. The name makes it clear that there is a change in the reinforcing fiber. But both FRP and GRP are normally used to denote the same plastic products.
Introduction
In recent years, FRP has been widely used in process, water and chemical industries due to their high resistance to corrosion.
FRP pipes are also increasingly used for the transport of Water, Oil, Fuel, Glycol, Wastewater, Sewer, etc. As a result, the demand for FRP pipes is continuously increasing.
The service life is usually very high, in the range of 50 years. Thus, the total cost of FRP pipes for life becomes cheaper as compared to metal pipes.
What is FRP?
The full form of FRP is a composite material consisting of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers. So, an FRP pipe is a pipe manufactured of FRP material by contact molding or filament winding method. Various types of resins like thermosetting polyester, epoxy, phenolic resin, etc are used to get specific FRP pipe properties in the final product.
The most widely used reinforcement is the fiberglass. As a corrosion-resistant alternative to metallic piping, the FRP piping system has found worldwide application.
Filament Wound Laminate
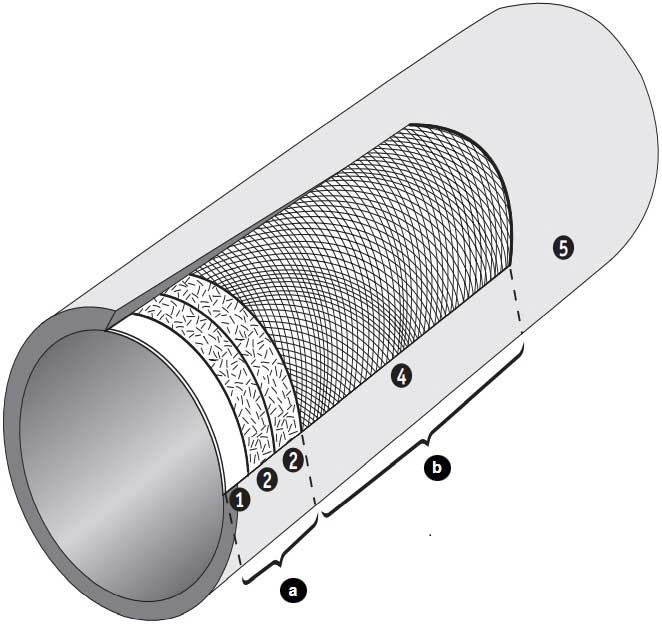
1 C-Glass surface veil
2 Chopped Strand Mat
3 Woven Roving
4 Filament Wound Strand
5 Outer surface layer with U.V. inhibitor
a Corrosion Barrier (Abrasion Barrier) (Thickness .100in nominal)
b Structural Wall (Thickness in accordance with pressure rating)
Contact Molded Laminate
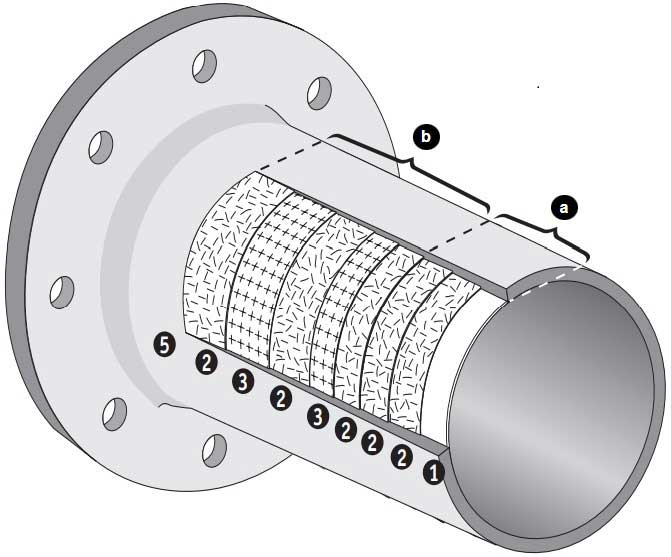
Common Fibers include:
- Glass is a very good insulating material and, when blended with the matrix, forms fiberglass or glass reinforced plastic. Compared to carbon fiber, it is both less strong and rigid and less brittle and expensive.
- Carbon based fiber reinforced plastics offer high tensile strength, chemical resistance, stiffness, and temperature tolerance along with low thermal expansion and weight. The carbon atoms form crystals which lie mostly along the fiber’s long axis. This alignment makes the material strong by making the ratio of strength to volume high.
- Aramid is a fiber component that results in robust and heat-resistant synthetic fibers. It finds wide applications in many industries.
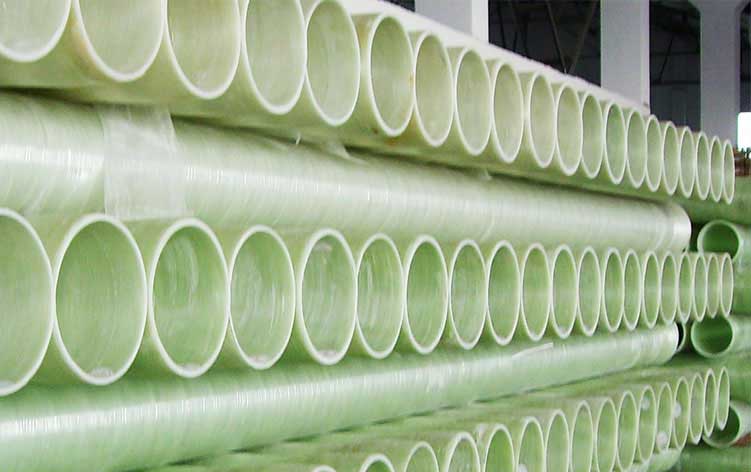 FRP Pipes
FRP Pipes
 FRP Flanged Fittings
FRP Flanged Fittings
By selecting FRP as the pipe and fittings materials, include flanges, elbows, tee's, crosses, reducers etc., the need for internal lining, external coating, and cathodic protection can easily be eliminated. FRP piping system is available in a wide range of sizes starting from 1 inch to above 100 inches.
More than just FRP pipe systems
Besides pipelines, storage tanks, towers, grids on walkways, profiles (like steel profiles) etc. are also manufactured from FRP. Below a description of a storage tank
Introduction
FRP storage tanks are divided into vertical storage tanks and horizontal storage tanks. The winding material selection of storage tanks must be appropriate, quality priority, and price consideration.
In the actual production, the tank wall structure of the FRP-wound storage tank is generally an inner liner layer, a strength layer and an outer surface layer.
Material and resin selection
Due to the different functions of the layers, the materials are selected differently, and the inner liner is directly in contact with the medium, and the material selection is correct or not, which plays a key role in controlling the leakage of the wound storage tank.
To use vinyl resin if store acidic medium, to use bisphenol A resin if store alkali medium, to use alkali-free glass fiber if need to be water and alkali resistant, to use medium-alkali glass fiber if need to be acid-resistant , and the inner liner is made of surface felt and chopped together to reinforce to increase the amount of glue and enhance the impermeability.
The strength layer mainly meets the strength and stiffness requirements of the storage tank. Material selection should fully consider that the selected resin matrix must have good penetrability with the glass fiber for winding to form a dense structural layer; the outer surface is in direct contact with the external environment, and the material is selected according to the aging resistance requirement.
Application:
FRP tanks can be used to store tanks of various media. They are resistant to pressure, corrosion, ageing, long service life, light weight, high strength, impermeability, heat insulation, insulation, non-toxicity and smooth surface. It is widely used in coatings, pharmaceuticals, building materials, chemicals, pigments, resins, food, scientific research and other industries.
Drawbacks of FRP
- FRP is not recommended for carrying fluid with temperature more than 100 degrees celsius
- Slight degradation from UV rays is found to occur which can be reduced by using pigments, dyes, UV stabilizers, fillers, etc in the resin system
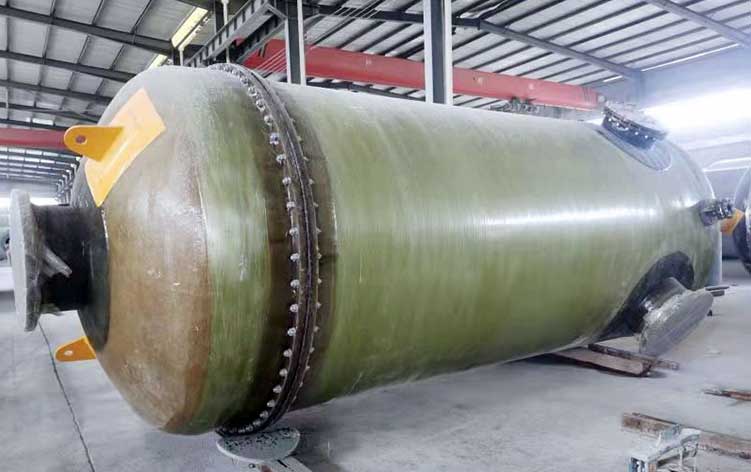 FRP Storage Tank
FRP Storage Tank
 FRP Columns
FRP Columns
 FRP Grids on walkways
FRP Grids on walkways
Reference(s) ..
www.frpwt.com
HeBei WeiTong FiberGlass Co., Ltd.
www.versteden.com
Versteden fiberglass piping systems
www.fibrex.com
FIBREX FRP piping systems
Some Codes and Standards for FRP
- ASTM D6041, Standard Specification for Contact-Molded “Fiberglass” (Glass Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) Corrosion Resistant Pipe and Fittings, ASTM. West Conshohocken, PA
- ASTM D2992, Obtaining Hydrostatic or Pressure Design Basis for Fiberglass (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) Pipe and Fittings. ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping. ASME, New York, NY
- ASTM D5421, Specification for Contact Molded Fiberglass (Glass-Fiber Reinforced Thermosetting Resin) Flanges. ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA
- ISO 7370, Glass fibre reinforced thermosetting plastics (GRP) pipes and fittings - Nominal diameters, specified diameters and standard lengths
- ANSI AWWA C950-2020, This standard describes the fabrication and the testing of nominal 1-in through 156-in (25-mm through 4,000-mm) fiberglass pipe and joining systems for use in both aboveground and belowground water systems. Service and distribution piping systems and transmission piping systems are included
- AWWA M45, Selection, installation, and maintenance of fiberglass pipe in potable water systems
- ISO 14692-1, Petroleum and natural gas industries - Glass-reinforced plastics (GRP) piping