HDPE Pipe & Fittings
HDPE pipe is a type of flexible plastic pipe made of thermoplastic HDPE (high-density polyethylene) created by the copolymerization of ethylene and small amounts of other hydrocarbons.
This type of plastic pipe has strong molecular bonds and high molecular density, making it resistant to aggressive chemicals. In addition, it does not leak or corrode and has many excellent advantages in terms of durability and strength.

HDPE pipe benefits
Corrosion resistance.. HDPE pipes are mainly used for transporting liquids and gases because they are not affected by the chemicals in the liquid or gas they transport. Thus, they do not cause leakage or clogging problems.
Resistant to high pressure.. HDPE pipes can withstand high pressure without deforming or damaging. Therefore, they can withstand the unstable water pressure of domestic water systems and wastewater conveyance systems.
Leak-free connections.. Unlike traditional metal piping systems, which are connected by mechanical joints. HDPE piping systems can be joined by heat fusion methods. In this method, two HDPE pipe surfaces are heated to a certain temperature, then the pipe cools, creating monolithic, permanent and leak-free pipe joints.

Longer life span.. The service life of HDPE pipes is longer than that of metal pipes (only 20 to 50 years). The estimated service life ranges from 50 to 100 years, depending on different applications.
Environmentally friendly.. HDPE pipes have minimal impact on the environment. HDPE pipes require less energy to produce than pipes made of other materials, and no hazardous toxic substances are released into the air during production.
Cost savings.. The cost of manufacturing and processing plastic pipes is lower than that of metal pipes. In addition, HDPE pipes are lightweight, saving more on transportation and installation costs.

How HDPE pipe is usually connected?
The principle of thermal fusion is to heat two HDPE pipe surfaces to a certain temperature and then fuse them by applying sufficient force. This force causes the fused pipes to mix with each other, resulting in fusion. After proper fusion, the joints are completely leak-proof. The joining surface is firmly equal to the tube itself in both strength and pressure properties.
There are four common joining methods for HDPE pipes, including butt fusion, socket fusion, saddle fusion and electrofusion.
Butt Fusion.. This is the most common welding method currently used for joining HDPE pipes. The two ends of the HDPE pipes are heated by using a butt welding machine to heat them to a certain temperature. Then they are pushed forward under proper pressure to fuse together. This technique produces a permanent, and flow-efficient connection.
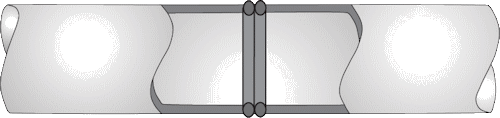

Socket Fusion.. This technique involves simultaneously heating the outer surface of the pipe end and the inner surface of the fitting until they reach a certain melting temperature, inserting the pipe end into the fitting and holding it in place until the joint cools. This method usually refers to connecting pipe to fitting rather than pipe to pipe.
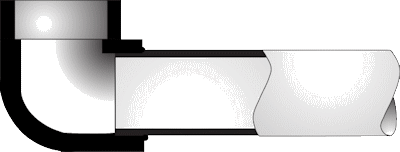

Saddle Fusion.. Saddle fusion is similar to socket fusion, but is used to attach a perpendicular fitting to the surface of a pipe. This consists of simultaneously heating both the outer surface of the pipe and the corresponding surface of the "saddle" fitting until both surfaces have reached the specific temperature. This can be performed using a saddle fusion machine designed for this technique.
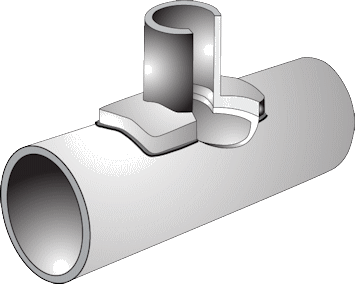

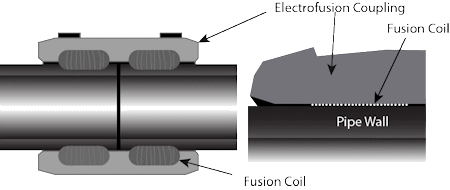
Electrofusion welding.. This joining technique for HDPE pipes is very different from the other fusion welding methods. The main difference is the way the pipe or fitting is heated. In normal fusion welding, a heating machine is used to heat the pipes and fitting surfaces. But the electrofusion joint is heated internally by a conductor or by a conductive polymer. Heat is created when an electric current is passed through the conductive material in the fitting. Then the tubes are cooled and will stick together.

Most Relevant HDPE Geothermal Standards
- ASTM F2206 - Standard Specification for Fabricated Fittings of Butt-Fused Polyethylene Plastic Pipe
- ASTM D2683 - Standard Specification for Socket-Type Polyethylene Fittings for Outside Diameter-Controlled Polyethylene Pipe and Tubing
- ASTM D2737 - Standard Specification for Polyethylene Plastic Tubing
- ASTM D3035 - Standard Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe (DR-PR) Based on Controlled Outside Diameter
- ASTM D3261 - Standard Specification for Butt Heat Fusion Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Fittings for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe and Tubing
- ASTM D3350 - Standard Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Pipe and Fittings Materials
- ASTM F714 - Standard Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe (DR-PR) Based on Outside Diameter
- ASTM F1055 - Standard Specification for Electrofusion Type Polyethylene Fittings for Outside Diameter Controlled Polyethylene and Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Pipe and Tubing
- AWWA C901-17 - Polyethylene (PE) Pressure Pipe and Tubing, 3/4 In. (19 mm) Through 3 In. (76 mm), for Water Service
- CSA B137.1 - Polyethylene (PE) Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings for Cold-water Pressure Services
- ANSI/CSA/IGSHPA C448 - Design and Installation of ground source heat pump systems for commercial and residential buildings
- NSF International Standard 358-1 - Polyethylene (HDPE) Pipe and Fittings for Water-Based Ground-Source Geothermal Heat Pump Systems
References.. europlas.com.vn / www.plasticpipe.org
Color or Stripe Color of PE Pipes
| Color | Application | Common Use |
| Blue | Potable & Drinking Water | Typically used for potable water supply. Not to be used for recycled or reclaimed water |
| Black | General Purpose, Stormwater & Fabricated Fittings | Typically used in general purpose, stormwater |
| Yellow | Gas - Town, Fuel, Coal, Seam Gas | Used extensively as either a striping or co-ex color for identification of gas, fuel gas and coal seam gas |
| Purple | Recycled/Reclaimed Water | Pipe for recycled/reclaimed water applications Branded as "RECYCLED OR RECLAIMED WATER DO NOT DRINK" WSAA specify - Striped for mains, striped or full co-ex for service lines |
| Red | Fire Service Water | Dedicated fire-extinguishing supply mains |
| Light Grey | Gravity Sewer | Typically used in gravity sewer applications. |
| Cream | Sewer Rising Main | Dedicated for pressurised sewer applications and specified by WSAA Branding must contain word 'SEWAGE' |
| White | Communications and Above Ground Mining | Used to identify communication conduits and in mining to reduce heat load on above ground transfer lines |
| Orange | Electrical Conduit | Used to identify electrical conduits and services |
| Green | Rainwater/Raw Water | Used as a striping color for rural water pipe used as a co-ex and with 'RAINWATER' branding for rainwater harvesting |
| Blue (B41 Bluebell) | Compressed Air (co-ex) | Same color as the potable water, used as a full outer co-ex Branding will have de-rating applied as per PIPA POP002 |
| Dark Blue | Compressed air (solid blue) | The global PE100 blue color to be used when making solid wall blue pipes. The only ISO9080 approved blue compounds are this color |
Related Post(s)

HDPE fittings such as elbows, tees, reducers and end caps are manufactured according to ASTM F2206 - Standard for Fabricated Fittings of Butt-Fused Polyethylene Plastic Pipe...

PE pipe can be divided into low-density polyethylene pipe (LDPE), medium-density polyethylene pipe (MDPE) and high-density polyethylene pipe (HDPE)...