American Society of Mechanical Engineers
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASME B31.3 Process Piping contains requirements for piping typically found in petroleum refineries; chemical, pharmaceutical, hydrogen, textile, paper and pulp, power generation, semiconductor, and cryogenic plants; and related processing plants and terminals.
ASME B31.3 Fluid Service Categories
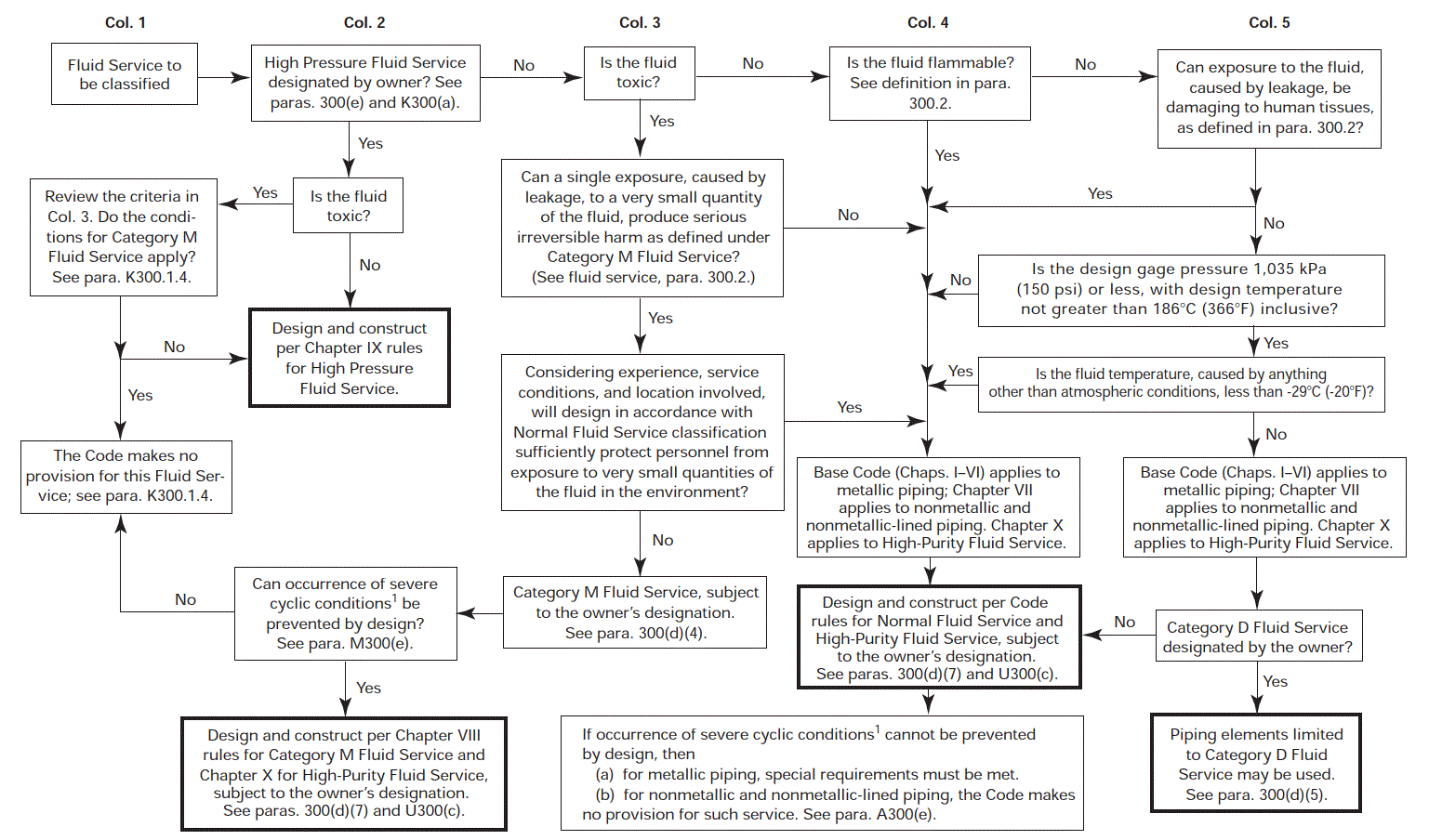
ASME B31.3 Fluid Service Categories are a set of criteria used to classify piping systems based on the hazard potential of the fluid being transported. This classification is important because it dictates the design, construction, testing and operating requirements for the piping system.
Fluid categories are a way to classify piping systems based on the hazards associated with the fluid being transported. The ASME B31.3 Process Piping Code defines six fluid categories..
- Category D
- Category M
- Normal fluids
- High-purity fluids
- High Pressure Fluid Service
- Fluid service at elevated temperature
It is the owner's responsibility to select the fluid service category. Selections of Category D or Category M cannot be made without the owner's permission. The fluid service is assumed to be Normal Fluid Service unless a different selection is made. Because some owners may not be familiar with this responsibility, the piping designer should inform the owner of the responsibility and may offer advice with respect to the selection process.
Category D Fluids
Category D Fluid Service is the least hazardous category and is usually reserved for fluids that are nonflammable, non-toxic and safe for human consumption. Examples of Category D fluid services include potable water supply, steam heating and chilled water systems.
Category D fluid services are reserved for the least hazardous fluids. These fluids are nonflammable, non-toxic and safe for human consumption. Examples of Category D fluids are..
Potable water, air, nitrogen, helium, potable water supply, fire protection systems, heating and cooling systems, compressed air systems, irrigation systems.
Category D pipeline systems are subject to less stringent design, examination and testing requirements than pipeline systems of other categories.
Guide to Classifying Fluid Services
Fluid Service Category M
Category M fluid service in which the potential for personnel exposure is judged to be significant and in which a single exposure of a very small quantity of a toxic fluid, caused by leakage, can produce serious irreversible harm to persons on breathing or bodily contact, even when prompt restorative measures are taken.
Examples of Category M liquids are..
Dealing with nerve gas, transportation of hazardous chemicals, processing of radioactive material, generation of nuclear energy, Phosgene, Hydrogen cyanide, Methyl isocyanate.
Category M piping systems are subject to the most stringent design, research and testing requirements.
Normal fluid supply: Normal fluid systems are used in a wide range of applications, including natural gas distribution, water distribution and chemical processing.
High-purity fluids: High-purity fluid systems are typically used in semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production and other industries where product contamination must be minimized. These systems must be designed and built to minimize contamination.
High pressure fluid system: High pressure fluid systems are typically used in hydraulic systems, compressed air systems and other industrial applications. These systems must be designed to withstand the high pressures and associated stresses.
Elevated-temperature fluid system: Elevated-temperature fluid systems are typically used in power plants, refineries and other industrial facilities. These systems must be designed to withstand the high temperatures and associated stresses.

The ASME B31.3 fluid service categories are an important part of ensuring the safety of piping systems. By selecting the correct fluid category, owners and engineers can design, build and operate safe and reliable piping systems.