Pipe line freezing
Pipe line freezing is a temporary method of insulating piping systems in which a freeze plug is made in the piping system so that the contents do not have to be drained. Pipe freezing is a valuable technique in the maintenance of all types of liquid storage, processing and transfer systems.
As a service, freezing lines for insulations have been on the market regularly since the 1970s, but the first patents were documented as early as the 1940s.
How pipe freezing works?
The basic theory behind a freeze plug is that the outer wall of the pipe cools to the point that the contents (usually water) form a plug inside the pipe, which attaches to the wall and forms solid insulation.
Tests have been done with plugs that could withstand more than 551 bar (8,000 psi.) To achieve freezing, a jacket is placed around the pipe, and liquid, usually liquid nitrogen, is circulated in it.
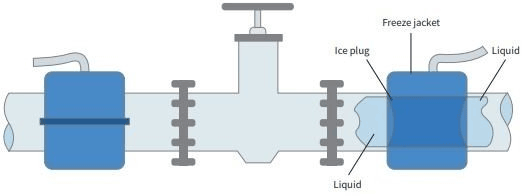 Image..www.hsos.eu
Image..www.hsos.eu
Earlier cloaks were essentially a closed empty space in which the liquid nitrogen came into direct contact with the pipe; modern cloaks operate more on the principle of heat exchange, with the liquid nitrogen circulating through veins in the cloak. The length of the jacket is usually twice the diameter of the pipe and about one inch thick.
Why choose pipe freezing?
Pipe freezing can often be a better solution when piping systems need to be repaired or replaced. This is because it is both a safer and faster alternative to hot tapping when applications call for it. There are many advantages of using the pipe freezing method. Pipe freezing methods are a non-intrusive alternative to developing temporary pipe insulation. Pipe freezing plugs do not require special welding or installation costs often associated with line stop fittings.
Another advantage of the pipe freezing method is that freezing time can be predicted based on pipe size, system conditions and ambient temperature. This allows for efficient planning of time and resource(s).
Examples of typical pipe freezing times..
- 1/2 in – 6 minutes
- 6 in – 48 minutes
- 8 in – 90 minutes
- 12 in — 3 hours
- 20 in – 4 hours
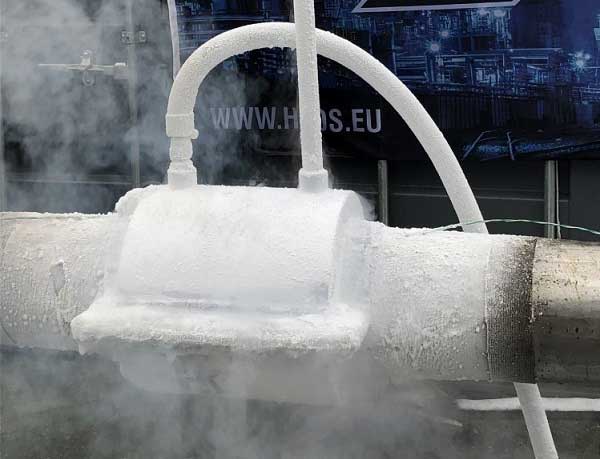 Image..www.hsos.eu
Image..www.hsos.eu
Limitations of the pipe freezing method
Pipe freezing is possible only when there is no flow and the pipe is full, as well as allowing sufficient expansion space for the collar, safe distance from welds, transitions and uneven metallurgy.
Health and safety when freezing pipes
Technicians from pipe freezing companies are trained and accredited with Gas Safety Training for the safe use of liquid nitrogen. Nitrogen makes up 78% of the air we breathe and is an inert gas. However, precautions must be taken because liquid nitrogen evaporates to gas 700 times its liquid volume. This is why risk assessments and method statements emphasize adequate ventilation.
Personal Protective Equipment
Reference(s).. https://ehs.uky.edu/ohs/cryogenic.html
Eye, hand, and body protection must be worn to prevent contact of liquid cryogens with the eyes or exposed skin. A hazard evaluation performed on each cryogenic operation will determine the specific personal protective equipment (PPE) required. The following are the minimum PPE requirements for cryogenic operations..
| Eyes | When pouring liquid nitrogen from a dewar, use non-vented chemical goggles or safety glasses with side shields. When working with liquid nitrogen in an open container or when transferring liquid nitrogen from a pressurized device, use safety glasses and a full-face shield. |
| Hands | When working on piping systems with exposed components at cryogenic temperatures, wear loose-fitting gloves made for cryogenic work (or leather welding type without gauntlets) to assure that skin will not freeze to cold pipes or metal parts. Loose-fitting gloves can be thrown off readily if cryogen is spilled into them. Small spills of liquid nitrogen, if not trapped against the skin, will usually evaporate without causing damage. |
| Feet | Wear closed-toe shoes that cover the top of the foot or boots with trouser legs extended over the top of the boot. |
| Body | Wear long-sleeved clothing made of non-absorbent material, cuff-less long trousers worn outside boots or over shoes, and an apron made of leather (or other appropriate material) when handling large quantities of cryogens. |
| Ears | Ear plugs or earmuffs may be required where excessive noise levels occur near filling and venting operations. |
Freezing a 4-Inch Pipe That's In Use to Add Isolation Valve
Emergency Procedures for Frostbite Injuries
The most likely cause of frostbite to the hands and body is contact with cold metal surfaces. Frostbite can be instantaneous if the skin is moist. Immediate treatment is vital. Report promptly to a medical care facility or call the national emergency number..
- Warm the affected area rapidly by immersion in water (not to exceed 105° F), body heat, or exposure to warm air.
- Calm the victim and avoid aggravating the injury. People with frostbitten feet should not walk on them. Do not rub or massage the affected parts of the body.
- If the eyes are affected, flush them with water for least 15 minutes.
- Always seek medical attention for frostbite injuries.

