Process instruments in Oil & Gas
Process instruments are essential components of any oil and gas operation. They are used to measure and monitor various aspects of the production process, such as pressure, temperature, flow and level measurement.
This article briefly describes, the three main types of process instrumentation used in the oil and gas industry, namely: electronic devices, analog devices and digital devices.
By understanding the different types of process instrumentation, operators can better maintain operations and ensure safe and efficient production.
Flow Meter
One of the most popular types of flow meters in the oil and gas industry is the Coriolis flow meter. These meters are used to measure mass flow rate, which is important for accurately measuring the amount of fluid moving through a pipe, also density, viscosity and temperature can be measured, giving users valuable insight into their operations.
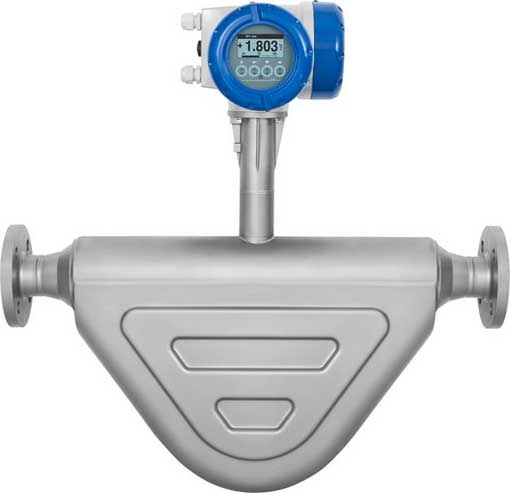 Coriolis mass flowmeter
Coriolis mass flowmeter Another type of flowmeter often used in oil and gas production is the ultrasonic flowmeter. Ultrasonic flow meters use sound waves to measure flow without physical contact with the fluid being measured. This makes them ideal for measuring hazardous or corrosive fluids without added risk.
 Ultrasonic flow meter
Ultrasonic flow meter Furthermore, vortex flow meters are an effective way to measure air or gas flow. These meters work by detecting pressure changes caused by the formation of vortices in a fluid as it flows through an obstruction in the pipe.
Vortex flow meters are especially useful when measuring turbulent fluids because they give accurate readings even under difficult conditions. With careful selection, the right flow meter can go a long way in optimizing oil and gas operations.
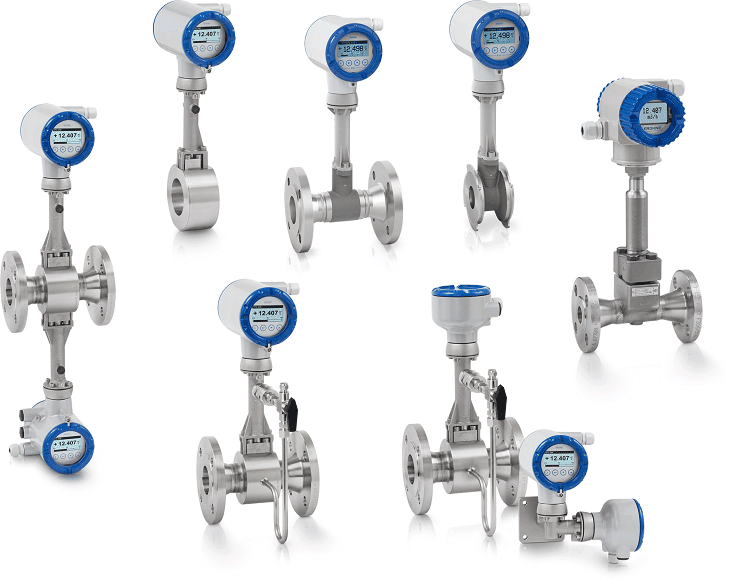 Vortex flow meters
Vortex flow meters Pressure Transmitters
There are three main pressure transmitters used in oil and gas operations: absolute pressure transmitters, membrane tight transmitters and differential pressure transmitters.
Absolute pressure transmitters measure the actual pressure of a gas or liquid and send this information to an electronic device.
Membrane-tight transmitters use a mechanical membrane to measure the pressure of a gas or liquid and send the information to an electronic device.
Differential pressure transmitters measure the difference between two pressures and convert this information into an electrical signal.
 Rosemount™ 3051C Smart Pressure Transmitter measures absolute, differential, and gauge pressures
Rosemount™ 3051C Smart Pressure Transmitter measures absolute, differential, and gauge pressures Each type of pressure transmitter has its own unique advantages for oil and gas operations. Membrane-sealed transmitters are cost-effective, reliable and require minimal maintenance. Differential pressure transmitters can be used to detect leaks in pipelines and vessels, while absolute pressure transmitters can be used to measure total pressure in hard-to-reach areas.
All three pressure transmitters are vital tools used in oil and gas operations. They help operators monitor and control systems, while also providing reliable readings that can be used to detect problems or potential problems.
Temperature Transmitter
Thermocouples are the most commonly used temperature transmitters. They measure temperature by detecting small differences in electrical potential between two dissimilar metals. However, thermocouples have a limited temperature range and can be affected by vibration and noise.
 Thermocouple
Thermocouple RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) measure temperature by electrical resistance. They offer higher accuracy than thermocouples, but also have a limited temperature range. RTDs are also prone to errors due to interference from electric currents or magnetic fields, so they should be placed away from such sources.
 Resistance Temperature Detector
Resistance Temperature Detector Thermistors are semiconductors that measure temperature by a change in electrical resistance. They are very accurate and have a wide temperature range, making them ideal for applications with high accuracy requirements. However, they must be calibrated, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
 Thermistors
Thermistors When choosing a temperature transmitter for oil and gas exploration, it is crucial to consider the environmental conditions and accuracy requirements of the application.
Radar level measurement
In non-contact level measurement with radar, the measuring instrument sends microwaves from above to the product, which reflects them back. Based on the microwave signals received by the measuring instrument, the distance to the product surface is determined and the level is calculated. With this measurement method, liquids and solids are measured.
 Radar level transmitters
Radar level transmitters The advantages of radar level measurement are, that the measurement is not affected by temperature, pressure and dust development. In addition, non-contact level measurement with radar is distinguished by a particularly high measurement accuracy.
Related Post(s)
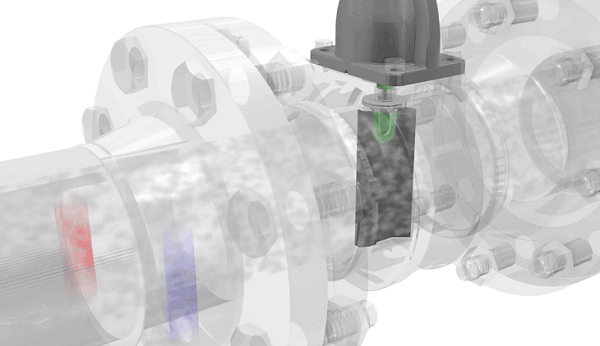
Vortex flow meters are transducers that determine the flow rate of a substance in a pipe section by analyzing a vortex line (von Kármán vortex)...