What are Turbine Flow Meters?
Turbine flow meters are one of the most popular and simplest methods of measuring flow. The turbine flow sensor is usually used to measure liquids, including chemicals and water, but also measures gas. The turbine flowmeter was invented in the 18th century by Reinhard Woltman and is reliable for both liquids and gases.
Working principle
Turbine flow meters work by using the energy of the fluid flowing through them to move a rotor in the water or other fluid flowing through it. This rotor has blades that are angled such that they use the fluid to create rotation and move the rotor clockwise or counterclockwise.
The rotor blades are attached to a rod, which can rotate using bearings. The faster the fluid flows through the turbine's flow meter, the faster the rotor blades rotate and, as a result, the faster the rod spins.
You can control how fast or slow the blades rotate by attaching a sensor or magnet to the blades. In the magnetic method, magnets are attached to the blades and as they rotate, they pass a small piece of metal embedded in the flow meter itself at some point.
In this way, the velocity of the fluid can be accurately judged by the time that elapses between each time the magnet makes contact with the piece of metal. The brilliance of this system is that these sensors can work in whatever direction the fluid is flowing through the turbine's flow meter.
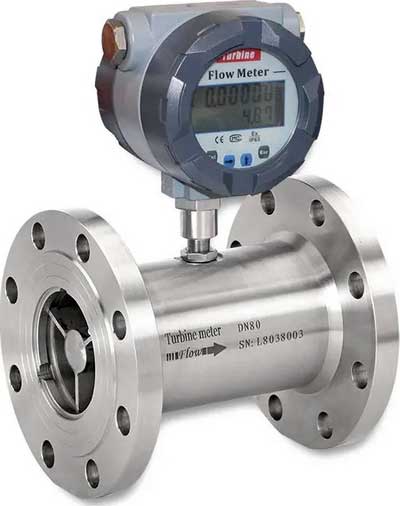

Variations in design and construction
Most industrial turbine flow meters are made of austenitic stainless steel, while turbine meters for municipal water services are bronze or cast iron. Rotor and bearing materials are chosen in accordance with the process fluid and service.
Rotors are often made of stainless steel and bearings of graphite, tungsten carbide, ceramic or in special cases of synthetic ruby or sapphire combined with tungsten carbide. In all cases, the bearings and shafts are designed to minimize friction and maximize wear resistance. Some corrosion-resistant designs are made of plastic materials such as PVC.
The insertion turbine gauge is similar to a pitot-tube differential pressure gauge and is a point velocity device. It is designed to be inserted into a liquid or gas line to a depth at which the small-diameter rotor reads the average velocity in the line. Because they are very sensitive to the velocity profile of the flowing stream, they must be profiled at various points in the flow path.
Technology and Working Principle of Turbine Flowmeters
Related Post(s)

The differential producing flowmeter or Venturi has a long history of uses in many applications. Due to its simplicity and dependability, the Venturi is among the most common flowmeter...