Types of Steam Traps
Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Thermodynamic steam traps have a unique operating principle which relies on the dynamics of water and flash steam. They are simple, robust and reliable and can operate up to very high temperatures and pressures. Their construction, use and benefits are detailed on this page.
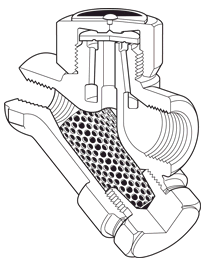
The thermodynamic trap is an extremely robust steam trap with a simple mode of operation. The trap operates by means of the dynamic effect of flash steam as it passes through the trap, as depicted in the image below. The only moving part is the disc above the flat face inside the control chamber or cap.
On start-up, incoming pressure raises the disc, and cool condensate plus air is immediately discharged from the inner ring, under the disc, and out through three peripheral outlets (i).
Hot condensate flowing through the inlet passage into the chamber under the disc drops in pressure and releases flash steam moving at high velocity. This high velocity creates a low pressure area under the disc, drawing it towards its seat (ii).
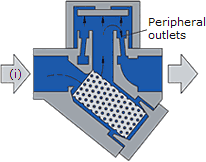
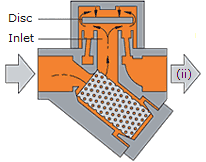
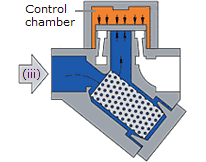
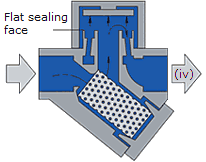
Operation of a thermodynamic steam trap
At the same time, the flash steam pressure builds up inside the chamber above the disc, forcing it down against the incoming condensate until it seats on the inner and outer rings. At this point, the flash steam is trapped in the upper chamber, and the pressure above the disc equals the pressure being applied to the underside of the disc from the inner ring. However, the top of the disc is subject to a greater force than the underside, as it has a greater surface area.
Eventually the trapped pressure in the upper chamber falls as the flash steam condenses. The disc is raised by the now higher condensate pressure and the cycle repeats (iv).
The rate of operation depends on steam temperature and ambient conditions. Most traps will stay closed for between 20 and 40 seconds. If the trap opens too frequently, perhaps due to a cold, wet, and windy location, the rate of opening can be slowed by simply fitting an insulating cover onto the top of the trap.
Advantages of the thermodynamic steam traps
- Thermodynamic traps can operate across their entire working range without any adjustment or change of internals.
- They are compact, simple, lightweight and have a large condensate capacity for their size.
- Thermodynamic traps can be used on high pressure and superheated steam and are not affected by waterhammer or vibration. The all stainless steel construction offers a high degree of resistance to corrosive condensate.
- Thermodynamic traps are not damaged by freezing and are unlikely to freeze if installed with the disc in a vertical plane and discharging freely to atmosphere. However, operation in this position may result in wear of the disc edge.
- As the disc is the only moving part, maintenance can easily be carried out without removing the trap from the line.
- The audible 'click' which occurs as the trap opens and closes makes trap testing very straight forward.
Thermodynamic steam trap
Disadvantages of the thermodynamic steam trap
- Thermodynamic steam traps will not work positively on very low differential pressures, as the velocity of flow across the underside of the disc is insufficient for lower pressure to occur. They are subjected to a minimum inlet pressure (typically 0.25 bar g) but can withstand a maximum backpressure of 80% of the inlet pressure.
- Thermodynamic traps can discharge a large amount of air on 'start-up' if the inlet pressure builds up slowly. However, rapid pressure build-up will cause high velocity air to shut the trap in the same way as steam, and it will 'air-bind'. In this case a separate thermostatic air vent can be fitted in parallel with the trap. Modern thermodynamic steam traps can have an inbuilt anti-air-binding disc which prevents air pressure building up on top of the disc and allows air to escape (image on the left).
- The discharge of the trap can be noisy and this factor may prohibit the use of a thermodynamic trap in some locations, e.g. outside a hospital ward or operating theatre. If this is a problem, it can easily be fitted with a diffuser which considerably reduces the discharge noise.
- Care should be taken not to oversize a thermodynamic trap as this can increase cycle times and induce wear. Mains drainage applications often only need to be fitted with low capacity versions, providing proper consideration is given to siting the drain pockets correctly.
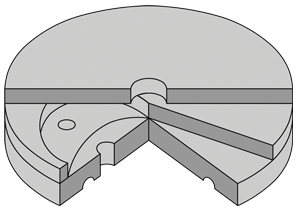
Anti-air-binding disc
Impulse steam trap
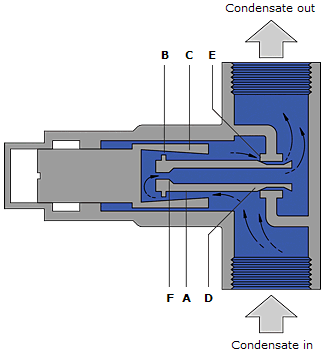
The impulse trap (as shown in the image on the right) consists of a hollow piston (A) with a piston disc (B) working inside a tapered piston (C) which acts as a guide. At 'start-up' the main Valve (D) rests on the seat (E) leaving a passage of flow through the clearance between piston and cylinder and hole (F) at the top of the piston. Increasing flow of air and condensate will act on the piston disc and lift the main Valve off its seat to give increased flow. Some condensate will also flow through the gap between the piston and disc, through E and away to the trap outlet.
As the condensate approaches steam temperature some of it flashes to steam as it passes through the gap. Although this is bled away through hole F it does create an intermediate pressure over the piston, which effectively positions the main Valve to meet the load. The trap can be adjusted by moving the position of piston (B) relative to the seat, but the trap is affected by significant backpressure. It has a substantial capacity, bearing in mind its small size. Conversely, the trap is unable to give complete shut-off and will pass steam on very light loads. The main problem however is the fine clearance between the piston and cylinder. This is readily affected by the dirt normally found in a steam system. The use of impulse traps is relatively limited.
Advantages of the impulse steam trap
- Impulse traps have a substantial condensate handling capacity for their size.
- They will work over a wide range of steam pressures without any change in Valve size and can be used on high pressure and superheated steam.
- They are good at venting air and cannot 'air-bind'.
Disadvantages of the impulse steam trap
- Impulse traps cannot give a dead tight shut-off and will blow steam on very light loads.
- They are easily affected by any dirt which enters the trap body due to the extremely small clearance between the piston and the cylinder.
- The traps can pulsate on light load causing noise, waterhammer and even mechanical damage to the Valve itself.
- They will not work against a backpressure which exceeds 40% of the inlet pressure.
Labyrinth steam trap
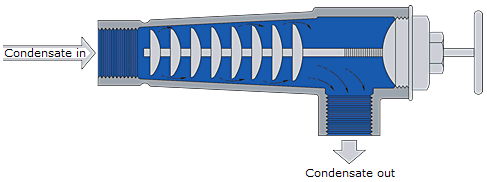
A simple form of the labyrinth trap is shown in the image below. It consists of a series of baffles which can be adjusted by means of a handwheel. Hot condensate passing between the first baffle and the trap body is subject to a drop in pressure and some of it 'flashes' to steam. The space around the next baffle has to cope with an increased volume of hot condensate and prevents the escape of live steam. The baffle plates can be moved either in or out using the handwheel, which alters their position relative to the body, effectively altering the overall size of the orifice.
Advantages of the labyrinth steam trap
- This type of trap is comparatively small in relation to its capacity and there is little potential for mechanical failure
since there are no automatic parts.
Disadvantages of the labyrinth steam trap
- The labyrinth trap has to be adjusted manually whenever there is a significant variation in either steam pressure or condensate load. If the setting is not right for the prevailing conditions, steam wastage or waterlogging of the steam space will occur (like a fixed orifice trap).
Reference(s) ..