Ball valves
A Ball valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve that uses a ball-shaped disk to stop or start flow. If the valve is opened, the ball rotates to a point where the hole through the ball is in line with the valve body inlet and outlet. If the valve is closed, the ball is rotated so that the hole is perpendicular to the flow openings of the valve body and the flow is stopped.
Types of Ball valves
Ball valves are basically available in three versions.. full port, venturi port and reduced port. The full-port valve has an internal diameter equal to the inner diameter of the pipe. Venturi and reduced-port versions generally are one pipe size smaller than the line size.
Ball valves are manufactured in different body configurations and the most common are..
- Top entry Ball valves allow access to valve internals for maintenance by removal of the valve Bonnet-cover. It is not required to be removed valve from the pipe system.
- Split body Ball valves consists of a two parts, where one part is smaller as the other. The ball is inserted in the larger body part, and the smaller body part is assembled by a bolted connection.
The valve ends are available as butt welding, socket welding, flanged, threaded and others.

Materials - Design - Bonnet
Materials
Balls are usually made of several metallics, while the seats are from soft materials like Teflon®, Neoprene, and combinations of these materials. The use of soft-seat materials imparts excellent sealing ability. The disadvantage of soft-seat materials (elastomeric materials) is, that they are not can be used in high temperatures processes.
For example, fluorinated polymer seats can be used for service temperatures from −200° (and larger) to 230°C and higher, while graphite seats may be used for temperatures from ?° to 500°C and higher.
Stem design
The stem in a Ball valve is not attached to the ball. Usually it has a rectangular portion at the ball, and that fits into a slot cut into the ball. The enlargement permits rotation of the ball as the valve is opened or closed.
Ball valve Bonnet
The Bonnet of a Ball valve is fastens to the body, which holds the stem assembly and ball in place. Adjustment of the Bonnet permits compression of the packing, which supplies the stem seal. Packing material for Ball valve stems is usually Teflon® or Teflon-filled or O-rings instead of packing.
Ball valves applications
The following are some typical applications of Ball valves..
- Air, gaseous, and liquid applications
- Drains and vents in liquid, gaseous, and other fluid services
- Steam service
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball valves
Advantages..
- Quick quarter turn on-off operation
- Tight sealing with low torque
- Smaller in size than most other valves
Disadvantages..
- Conventional Ball valves have poor throttling properties
- In slurry or other applications, the suspended particles can settle and become trapped in body cavities causing wear, leakage, or valve failure.
Deadman Handle

A deadman's handle on a valve, also known as a spring return handle, serves a specific purpose. Without this handle, tasks such as extracting media from a vessel or tank, adding additional media or performing tasks where an unattended valve should not be left open would be quite difficult. A dead man's handle makes it easy.
The true origin of the nickname deadman handle may be impossible to ascertain, but the meaning is quite simple. Basically, this morbid joke meant that if an operator died suddenly, the lever would move automatically, despite the tragedy. In this way, a valve - let's use a ball valve - equipped with a deadman's lever will automatically close itself when you release the lever. This is because of the spring action. Without the pressure against the spring, the lever will return to its original position.
![]()
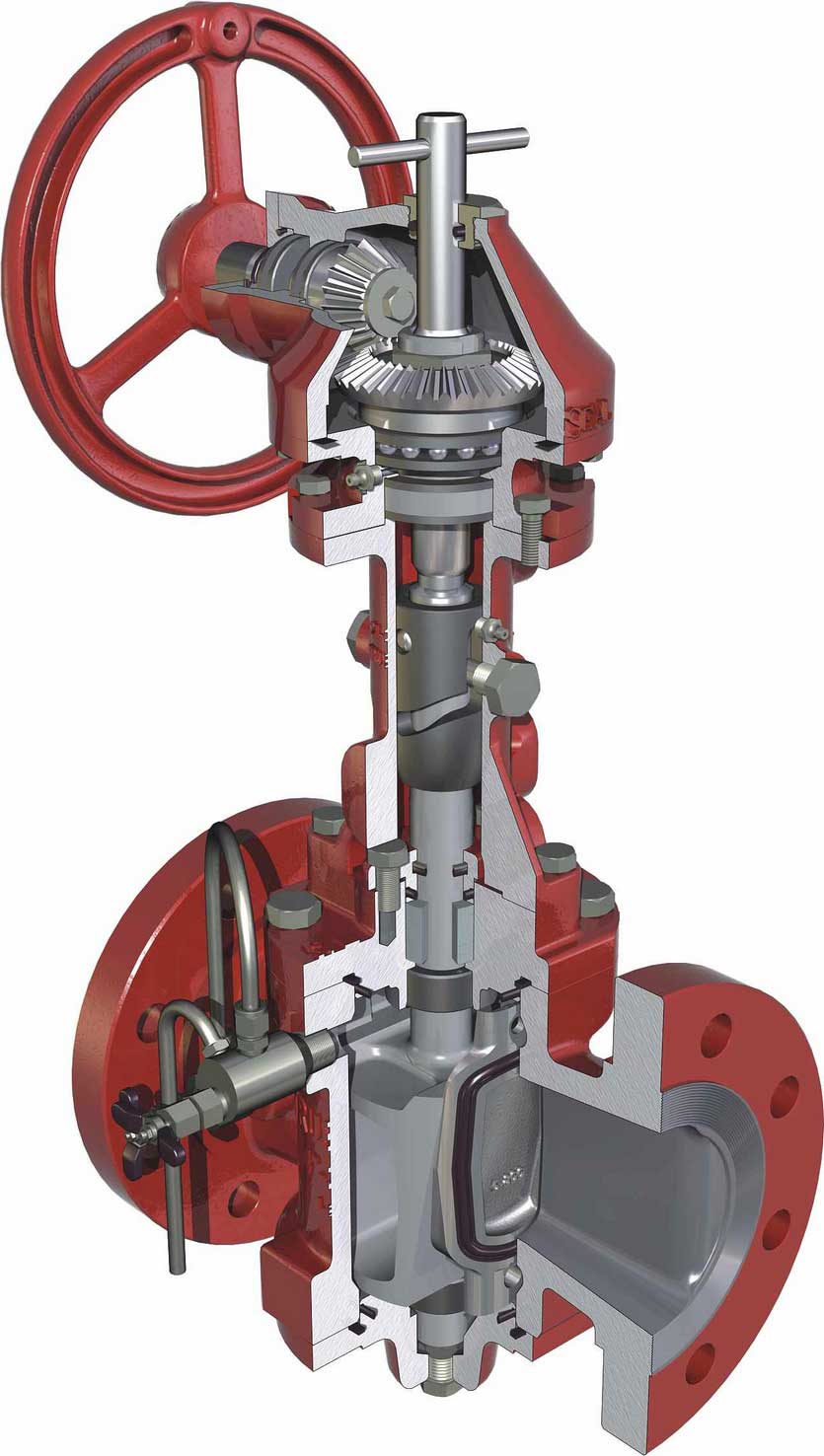
Cast steel trunnion ball valve
LARGE IMAGES OF VALVES
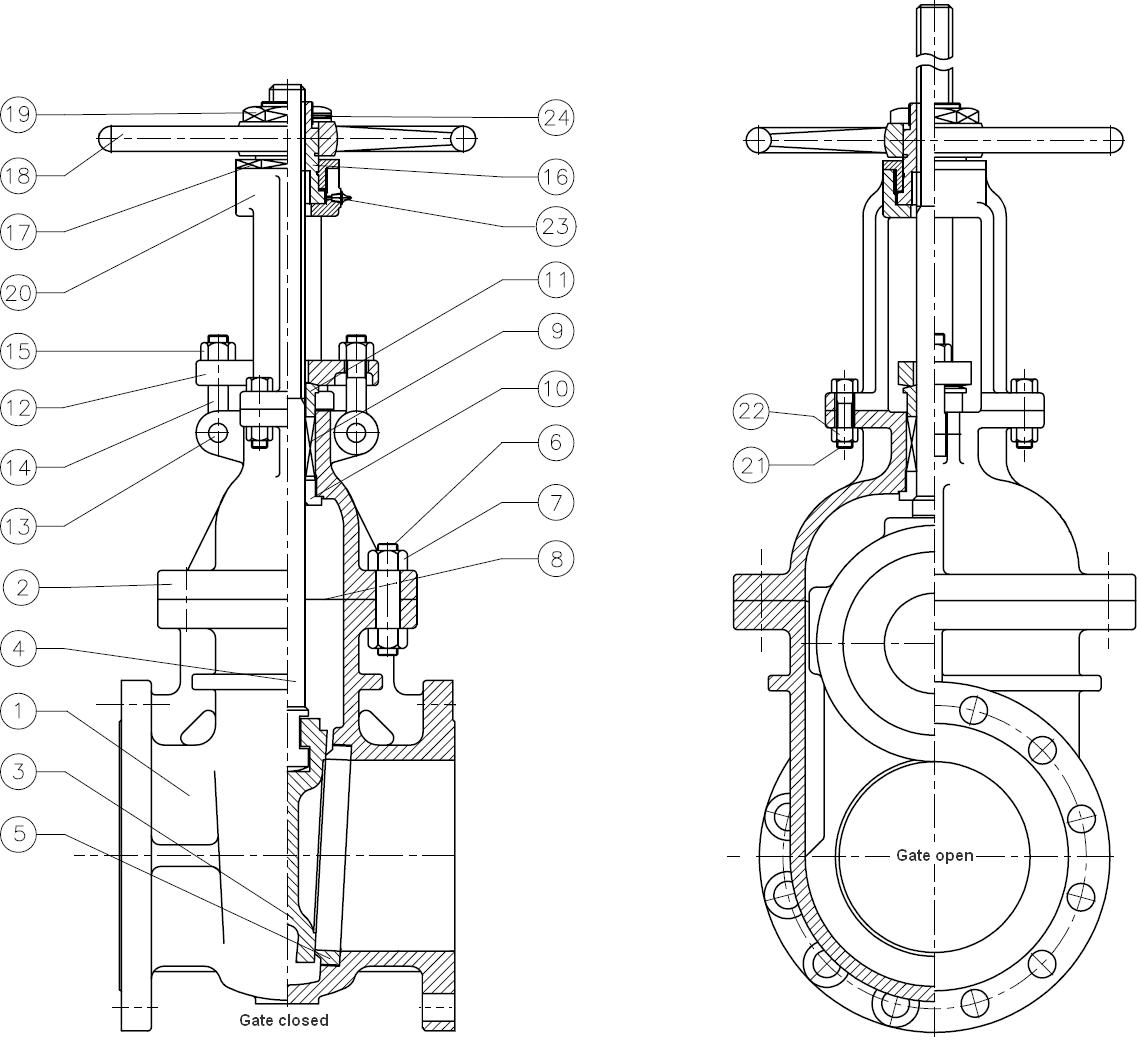
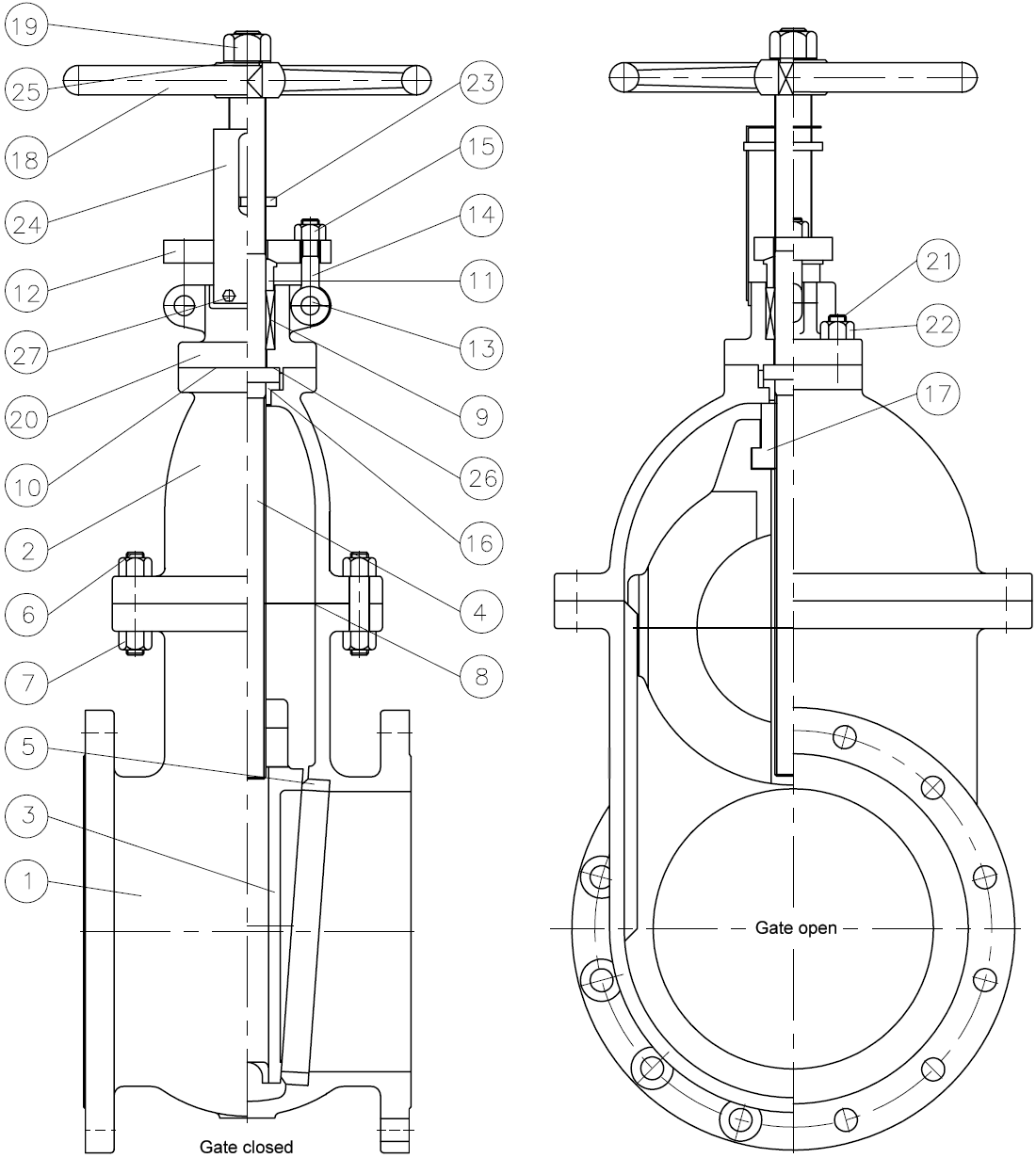
For a valve of the Rising Stem type, the stem will rise above the handwheel if the valve is opened. This happens, because the stem is threaded and mated with the bushing threads of a Yoke...
For a valve of the non Rising Stem type, there is no upward stem movement if the valve is opened. The stem is threaded into the disk. As the handwheel on the stem is rotated, the disk travels up or down...
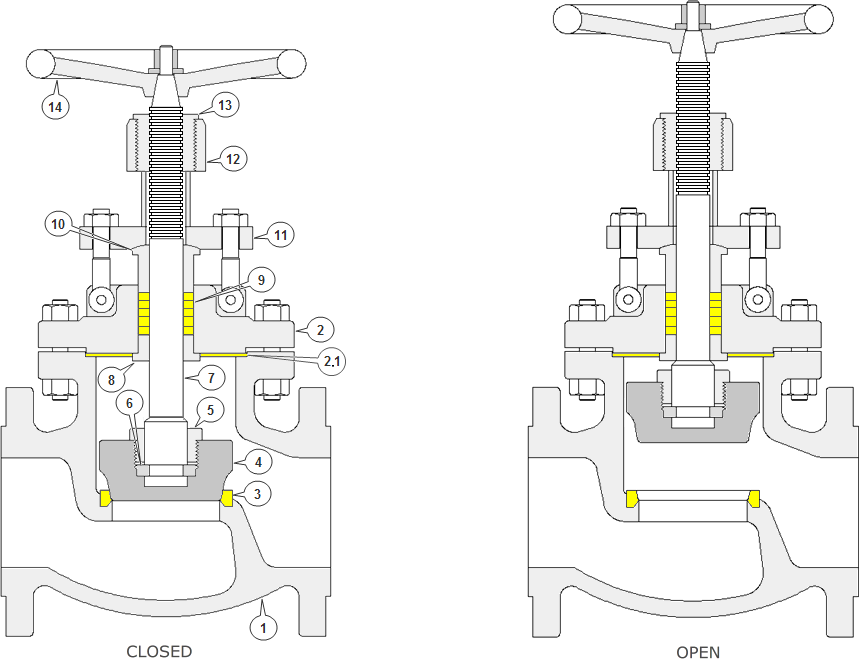
Globe valves usually have rising stems, and the larger sizes are of the outside screw-and-yoke construction. Components of the Globe valve are similar to those of the gate valve...
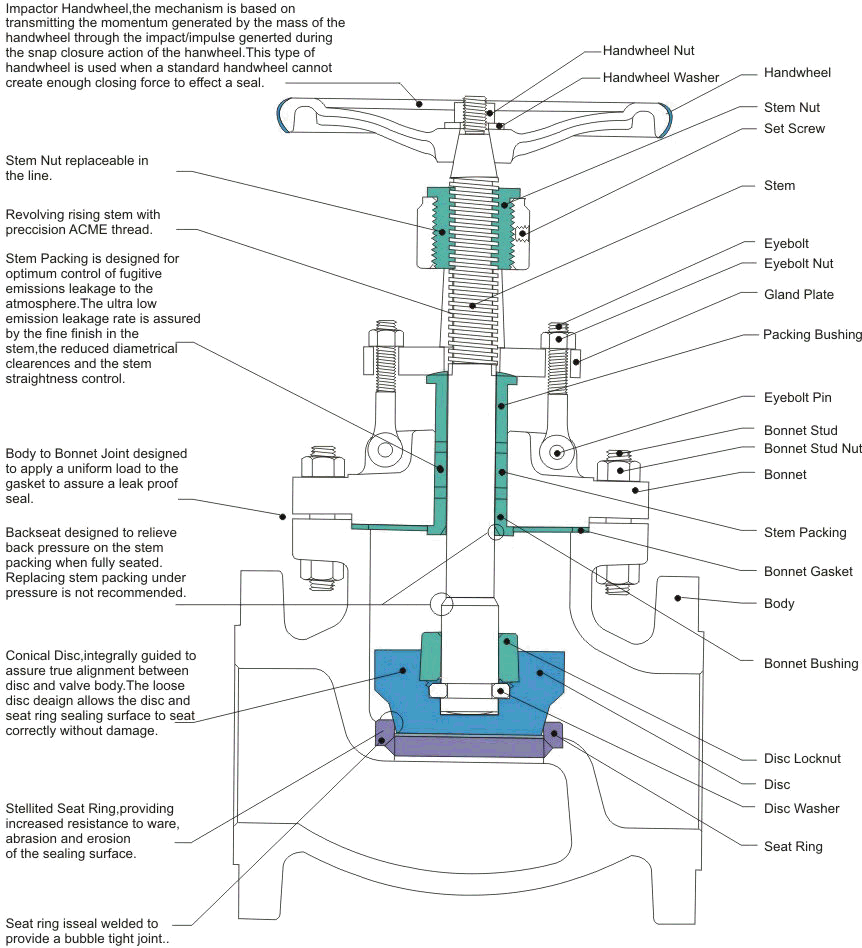
A Globe valve is a linear motion valve and are primarily designed to stop, start and regulate flow. The disk of a Globe valve can be totally removed from the flowpath or it can completely close the flowpath...
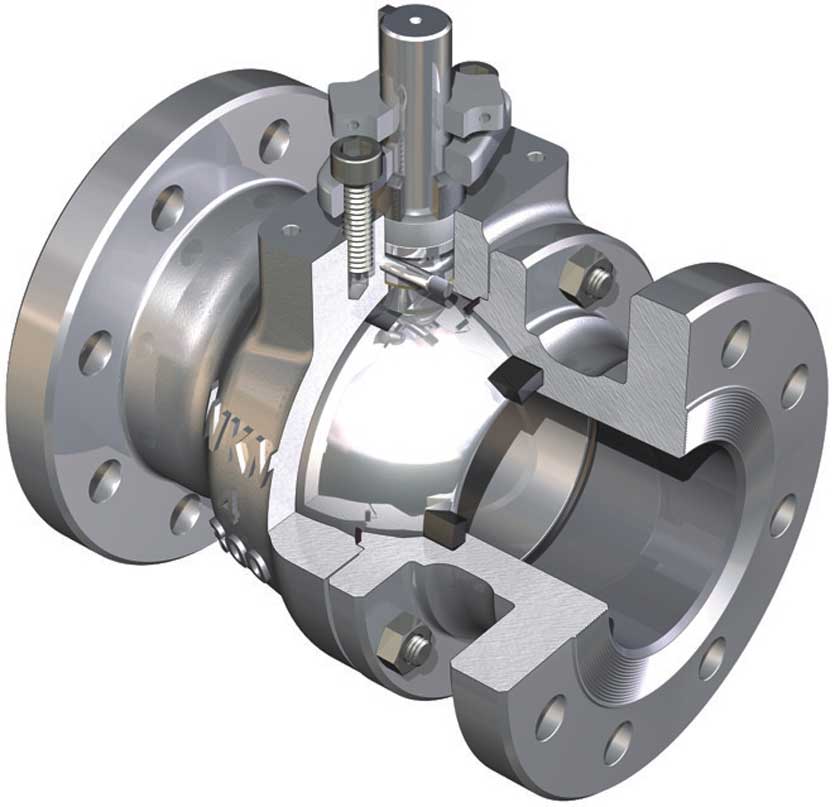
A Ball valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve that uses a ball-shaped disk to stop or start flow. If the valve is opened, the ball rotates to a point where the hole through the ball is in line with...
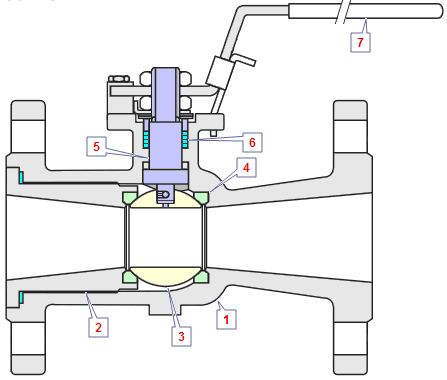
Ball valves are basically available in three versions.. full port, venturi port and reduced port. The full-port valve has an internal diameter equal to the inner diameter of the pipe...
A Plug Valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve that use a tapered or cylindrical plug to stop or start flow. In the open position, the plug-passage is in one line with the inlet and outlet ports of the valve body...
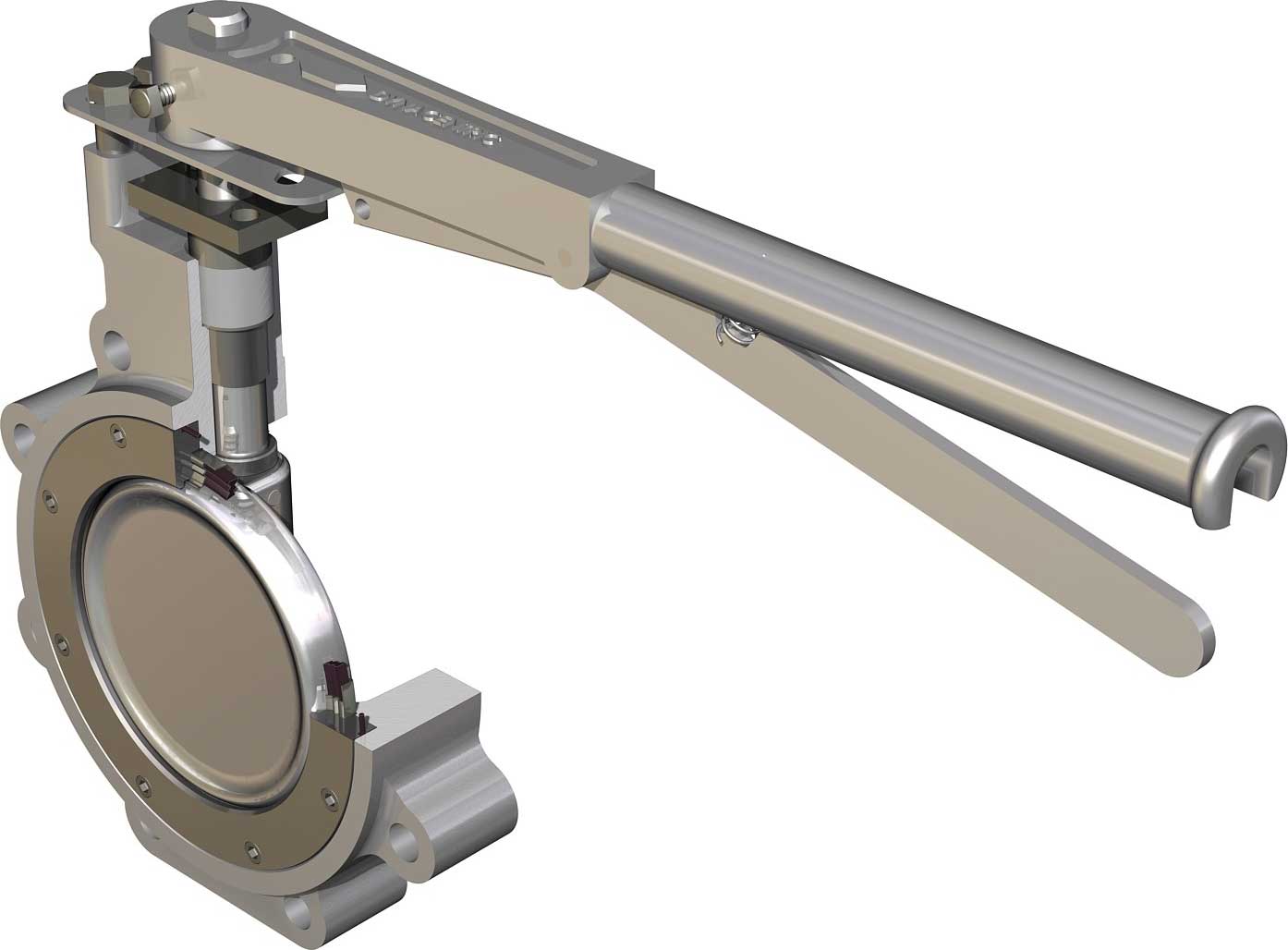
A Butterfly valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve, that is used to stop, regulate, and start flow, and are easy and fast to open...
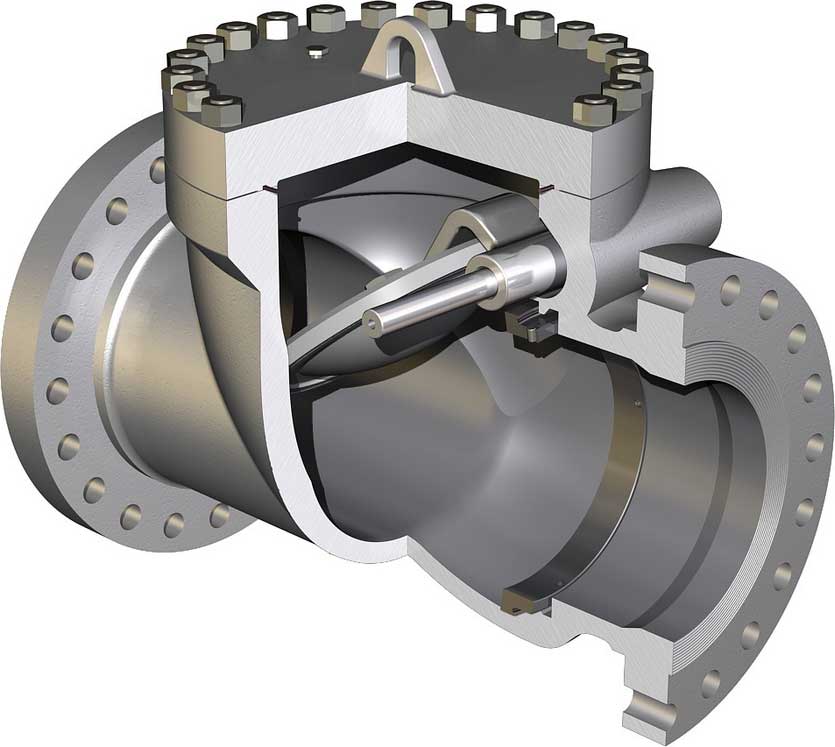
A basic swing Check valve consists of a valve body, a bonnet, and a disk that is connected to a hinge. The disk swings away from the valve-seat to allow flow in the forward direction...
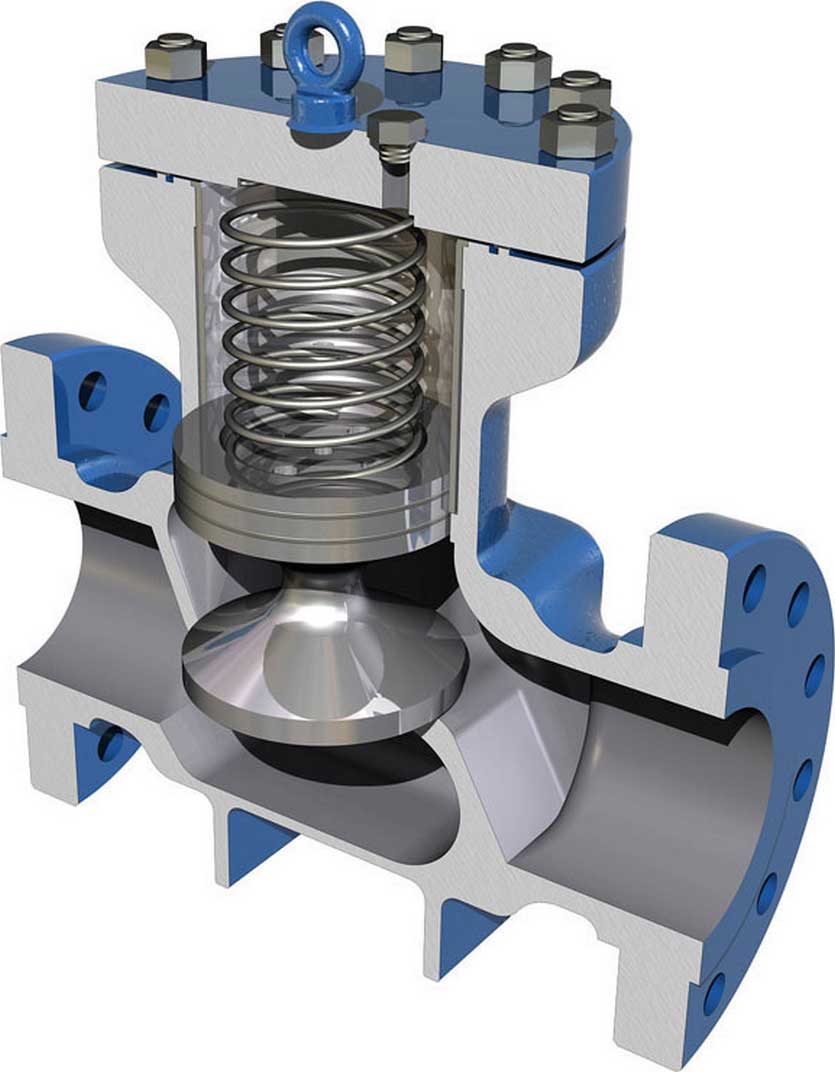

The seat design of a lift-check valve is similar to a Globe valve. The disc is usually in the form of a piston or a ball. This valves are particularly suitable for high-pressure service where velocity of flow is high...